|
Introduction
Overview
Computer requirements
Packet Engine Pro
Configure AGWPE
Download and Install
Basic AGWPE Setup
2 Radio Setup
2 Card Setup
Sound Device Setup
Basic Device Settings
Rename Sound Device
Additional Settings
Using the Tuning Aid
Problems?
Program Behavior
Receiving
Transmitting
Connections
Firewalls
AGWPE Features
AGWPE on a Network
Baud Rates & Modes
Remote Control
TCP/IP Over Radio
Tips and Tricks
Traffic Parameters
Compatible Programs:
Setup Help
Radio Interface
Getting Started
Kits and Pre-assembled
USB SignaLink
Receive Audio Cable
Transmit Audio Cable
PTT (TX Control) Cable
2 Radio Modification
About Packet
Packet Overview
Exchange Modes
TNCs and AGWPE
What
To Do with Packet
Common Frequencies
Frame Headers
Further Reading
|
|
Using AGWPE Over a Network
IP Address of AGWPE
Computer
Configure AGWPE
Configure Client Applications
Allowing Remote Access to AGWPE
It is possible to run AGWPE on one computer on a
network and have it send packets to and from applications on
other
computers on the network. The usual application is a home/local
network, but you can even configure AGWPE to work with computers
across
the internet!
Note:
This data exchange will work
only if your application program uses the TCP/IP
interface to interface with AGWPE. Programs such as
WinPack don't use the TCP/IP interface. They use the DDE
interface, so they can not do this. (UI-View can be
configured to use either the TCP/IP or DDE interface to
link to AGWPE.)
A work-around for WinPack users:
purchase the
PE Pro version for both the local and remote sites and
use PE Pro's radio port sharing
feature. With this feature, instances of PE Pro can share
radio ports and thus the radios and TNCs on those ports. So,
WinPack could link to an instance of PE Pro running on the
same computer and that instance of PE Pro could then link to
an instance of PE Pro running on a remote computer
that has been configured to "share" its radio ports.) |
First, some definitions:
-
host -
the computer running AGWPE
-
server - a device or
application that can exchange data with other devices or applications.
When AGWPE is configured to send and
receive data over a network to other applications, it is acting as a
server application.
-
client - any computer
/ application wishing to access the
AGWPE server.
-
IP Address - a number
with three dots in it, for example 192.168.0.1 or 169.254.0.1, which is
assigned to each computer connected to a network. IP
Addresses are needed to router data across networks running TCP/IP
protocols (which most local networks do).
-
port number - an
extension of the IP address. TCP ports are simply number codes used by
the Windows TCP/IP protocol to associate any TCP/IP data exchanges with
a particular program (or service) running on the computer. (They are not
physical ports on the computer.)
Second, a caution: This page will not be able to discuss all
possible network configurations. You will need to adapt this basic
explanation
to match the specifics of your ISP (Internet Service Provider), your
network hardware, and any installed network software, including Windows
network configurations.
To start, make sure you
have AGWPE running successfully on the host and that your network
connection is running correctly.
1.
Obtain the
IP Address
of the
host computer where AGWPE is running.
Your host computer will have three IP addresses of importance:
- a local address
of 127.0.01 or "local host", which means "this computer". This is
the address you would use to connect to AGWPE if the client
application is running on the same computer
as AGWPE.
- a private IP address
such as 192.168.x.x. This is the address someone would use to
connect to AGWPE if the client application is running on a
different computer but on the
same local area network, e.g. your home network.
- a public IP address
which is assigned by your Internet Service Provider. This is the
address someone would use to connect to AGWPE if the client
application is running on a remote computer on
a different network or over the internet.
A. Learning the private IP
address of a computer on your home network :
- Windows 95/98/ME: from the Windows'
Start button, select
Run, then in the Open box, enter
winipcfg and press OK.
In the resulting
window, note the IP Address. Press
OK to exit.
- Windows XP/NT: from the Windows'
Start button, select
Run, then enter CMD
to bring up a DOS window and prompt. Enter
ipconfig and in the
resulting window, make a note of the IP Address.
Then enter Exit to close the DOS window.
Note: A computer's IP address may change every boot-up if Windows
is set to obtain an address automatically from the network router each time it
starts. This is called dynamic addressing.
You can also assign an unchanging "static" IP address to the computer (see
Windows' Help for advice on how to do this: search for "static
address" or "specific IP address"). This may be useful if you use AGWPE regularly on a
private network.
B. Learning the public IP
address of a computer as it is identified on the internet:
|
Note that if your subscription is for a
dynamic IP address, your public IP
address can change each time you connect to the ISP. This can be
a problem for others trying to connect to you; they would have
to ask you for your current public IP address. If you don't want
to pay for a static (unchanging) IP
address, you can subscribe to a "dynamic DNS" service that
will automatically link your clients to your current dynamic IP
(see Dynamic DNS Service below)
|
- If you are connected directly to a broadband (DSL, cable. etc.) modem, use
the method described just above in "A." to learn your public IP
address.
- Another way to learn you public IP address is
to send an email to yourself. Look for your IP address in the
headers* of the email you receive back. Look for the
bottom-most header line that begins with "Received:"
(there may be several "Received:" lines.). For example:
- Start AGWPE and call up the AGWPE menu
(right click on AGWPE System tray icon
 )
)
- Select Setup Interfaces. This brings up
the Winsock and HTTP Interface Setup
window and the WinSock Interface tab.
- Make sure the Enable
Winsock TCP/IP Application Interface is checked (default
setting) and, in the Setup section, note the
TCP Port number. Leave the port number at
the default of 8000 unless you have
other software running in your computer that also uses that port
(this would be unusual). If another application is using that port, you
can configure AGWPE to use a different port number.
- Now click on the WinSock
Interface Security tab.
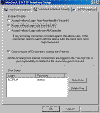 <-- Click to enlarge
<-- Click to enlarge
Note the three enable/disable connection options at the top of the screen. These
options
control which clients can access AGWPE on the
host
computer and whether or not
they need to use a LOGIN name and PASSWORD to gain access.
For example, the second choice specifies that:
-
clients on your local
area network (LAN) can use the host's AGWPE server
without a LOGIN name or PASSWORD,
but
-
clients outside of the LAN can use AGWPE only
with a LOGIN and
PASSWORD that matches an entry in the
User Setup list at the bottom of the
WinSock
Interface Security screen. (Use the New
User button next to the list to add LOGIN and PASSWORD
for other users.)
Note: If you are
thinking of controlling access by using LOGIN name and PASSWORD, be aware that
most AGWPE-compatible programs are
not
able to send a LOGIN and PASSWORD, so they wouldn't be able to get
access to AGWPE over a network. Even AGW's programs don't have this
provision! In fact, as of March 2005, I believe that
only UI-View and PacLink have such a provision.
- Press the OK button
to save the changes. AGWPE will now act as a
server.
For a way to test your TCP/IP
connection to AGWPE, see the
TCP/IP Settings page
on this website
|
3. Configure your packet application on the
client computer so it can find the
host computer and the AGWPE
server
on the network.
Only applications that connect to AGWPE with the TCP/IP protocol can be configured to do this.
Those that use the DDE protocol to link to AGWPE cannot, for example, WinPack.
As examples, here's how to do it for 4 applications that can,
UI-View, WinAPRS,
APRSplus and
AGWTerm.
-
a. UI-View:
From UI-View's top menu bar,
select Setup>Comms Setup. In the
Comms Setup window, for
Host Mode select AGWPE. When you do, a
Setup button
will appear next to the AGWPE field. Press that button to reveal the
AGWPE Setup window.
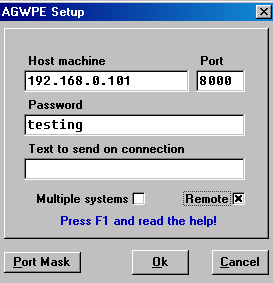
Please -- as the screen note suggests -- press
F1 to read the Help
file. Roger, G4IDE, the program author, has some terrific additional
information in the file.
-
For the Host Machine,
fill in the IP address of the host computer
running AGWPE which you identified in #1.
above.
-
The Port number should be 8000
unless you elected a different port in #2. above.
-
The
Password can be left blank unless you
turned on security in AGWPE as described in #2. above.
If you did, enter the password.
(Note for UI-View users: if AGWPE is using security, UI-View
sends your call sign as the LOGIN name all in
upper case
letters, minus any SSID number, for example, NM5RM-4 is sent as NM5RM.
Therefore, when you create a LOGIN name in AGWPE, it should be the
callsign used in UI-View in upper case letters, minus any SSID.)
-
The Text to send on connection can be
left blank.
-
Generally, the Multiple
Systems check box can be left blank unless you want to connect to
more than one remote instance of AGWPE. Press F1 for more info about this feature.
-
The Remote check box can be left blank unless the AGWPE host is not
on your LAN. Again press F1 for more
information; also see #4. below).
-
The Port Mask need not be
changed. By default, no ports are masked, i.e. UI-View will use all
AGWPE ports it finds. You would use this option only to limit the AGWPE
ports that UI-View will use to get data. For example, if AGWPE Port 1
is on a VHF frequency and AGWPE Port 2 is on an HF frequency and you
want only VHF data, you would use the Port Mask to limit data to just
AGWPE port 1.
-
b. WinAPRS: You first need to create a new .prt
file in the PORTS folder under the main WINAPRS folder. It might
be helpful to read the basic WinAPRS/AGWPE
configuration page on this site for advice on how to do this.
The name of this file might be AGWPE_LAN.prt or something similar --
your choice. The file contents would similar to:
// Created by Me on 10/1/2002
NAME AGWPE on My LAN
TYPE TCP
PARSER AGWPE
HOST 192.168.0.101:8000
BAND VHF
PATH WIDE,WIDE2-2
AGWTNC 0
Remember that the field name -- the first word in each sentence
( e.g.
PARSER) is separated from the following word ( e.g. AGWPE) by a
TAB
character not a space.
The key items in this file are:
NAME: Enter your choice of a port description.
This is what will be displayed in WinAPRS.
HOST: Enter the IP address of the
host
computer (see #1.
above ) and the AGWPE server TCP port number (see
#2. above)
PATH: Enter the PATH you want AGWPE to use
when it sends out a packet.
AGWTNC: Enter the AGWPE radio port you want
to use. Use 0 for AGWPE port 1; 1 for AGWPE port 2; etc.
After this file is created and saved in the
PORTS
folder, restart WinAPRS. From WinAPRS's top menu, select
Settings, then Port
List. In the resulting Port Definitions
List window, you should now see a port with the
NAME you entered in .prt file. Click on
that port and then click on the Open button
at the top of the window to activate it. If everything works correctly,
then the Status, Open
# and Comments fields will
all fill in, indicating that WinAPRS has
successfully found the AGWPE server (if the Comments field remains blank, there is a problem):
 <-- Click to enlarge
<-- Click to enlarge
Note that WinAPRS has no way to send a LOGIN or PASSWORD to AGWPE, so it
will not work with AGWPE over a network if you have AGWPE set to check for passwords.
You can create additional .prt files to link to
additional remote computers.
-
c. APRSplus:
The critical setting is in the
KipSSPE program. Start that program and look for the
IP Address field at the bottom of the
screen. Enter the host's IP address (as determined in
#1.
above)
in this field.
Note that APRSplus has no way to send a LOGIN or PASSWORD to AGWPE, so
it will not work with AGWPE over a network if you have AGWPE set to check for
passwords.
-
d. AGWTerm:
First,
please note that SV2AGW has created two versions of AGWTerm. If you want
to run AGWTerm over a network, you must use the
TCP/IP version (download
Agwtermtcp.zip dated 14Feb2002 to find a AGWTerm.exe file dated
16Aug2001) .
In the folder where install AGWTerm, you will find
a file called AGWterm.ini (this file is
only created after you run AGWTerm for the first time). Use a text
editor, such as Notepad, to open this .ini file. By default,
AGWTerm creates an IP address entry (what it calls SOCKSADR) that assumes the AGWPE will be running on the same
computer as AGWTerm, i.e. localhost. This
is an alias for an IP Address of 127.0.0.1, which is a special IP address
that means "this computer". It also assumes that you are using the
default AGWPE server TCP port address (what it calls
SOCKSPORT) of
8000 (see
#2. above).
[Packet]
SOCKSPORT=8000
SOCKSADR=localhost
<-- change "localhost" to
IP address of host
example: 192.168.0.2
see
#1.
above
Note that AGWTerm has no way to send a LOGIN or PASSWORD to AGWPE, so
AGWTerm will not work with AGWPE across a
network if you have AGWPE set to check for
passwords.
- a.
Dynamic DNS Services:
If you want to let clients outside of your LAN
access the AGWPE server, they will need to know the IP address assigned to
your computer or network by your ISP (Internet Service Provider). If your
subscription to your ISP is for a dynamic IP address, your public IP address can change each time you connect to
the ISP. This can be a problem for others trying to connect to you; they
would have to ask you for your current public IP address.
If you don't
want to pay for a static (unchanging) IP
address, you can subscribe to a "dynamic DNS" service that will
automatically link your clients to your current dynamic IP:
-
First, obtain a personal domain name (for
about USD $35/year).
Example: www.sv2agw.org
-
Then, find a dynamic DNS (domain name system)
service that will match your domain name with your current dynamic
IP network address. This is done by running a special utility from
the service which periodically contacts the service over the
internet to tell it the dynamic IP address your AGWPE computer has
been assigned. Users then can just enter your personal domain name
to connect to you; they need not worry about entering your actual
network IP address. The dynamic DNS service will make the
translation.
To find a dynamic service provider, do a web search for "dynamic
DNS". Some offer free services or free services if you buy your
domain name from them.
- b. Firewalls and security considerations: If your
computer or local network has
an open internet connection, you should be taking precautions to prevent
unauthorized access to it. Gateways or routers may have an integrated firewall, or you can use a
firewall program, such as Zone Alarm, McAfee Firewall, Norton Personal
Firewall or even Windows XP's internal Internet
Connection Firewall.
Note that firewalls will also prevent outside access to
the AGWPE server, unless the firewalls are configured to permit an exception
for the AGWPE server. You will need to read the documentation for your
firewall to learn how to do this. For example, my router has a place where
I can configure "Virtual Servers" and another one that has
"Port Forwarding". I specify the port I want to open
(8000) and the IP address of the computer that will handle that port,
which is the 192.168.x.x address of my AGWPE computer.
Explaining how to do this for each
possible firewall or gateway is beyond the capabilities of this web site, but here
are some considerations when allowing remote access:
-
The firewall should limit remote access solely to the
computer running AGWPE
and solely to that computer's port 8000; do not allow access to other
computers on your network or to other.
-
Remember that a remote user who achieves access to
the AGWPE server can use it to both receive and
send packets. In effect the
remote user will gain control of the radio connected to AGWPE and will be
able to initiate transmissions. In most
countries, this has a serious implication -- you will be held accountable for
any transmissions made by others using your radio.
For this reason, you may want to configure your firewall to limit incoming
access from specific, trusted IP addresses. In addition, you should use
the LOGIN / PASSWORD security feature in AGWPE (see
#2. above) if the
client's application can send them ... but remember most applications can
not.
|