Configuring Your Computer as a TOR Gateway
Using a TOR Gateway: An Example
Gateway Configuration
Alternative Configuration using a Proxy Server Program
A "gateway" TCP/IP over Radio (TOR) station is one that has access to the
internet and is willing to relay internet data by radio to and from client
stations who do not have access to the internet.
NOTE: TOR only works on Windows XP
and earlier versions.
Let's assume SV2BBO
(a client station) does not have access to the internet,
but a
nearby station, SV2DFK, does have dialup access to the
internet and is willing to act as SV2BBO's
internet gateway. The stations already know that
they can exchange standard AX.25 packets by
radio.
Both stations have also configured their
computers to use the TCP/IP Over Radio (TOR)
feature:
|
Note:
AGWPE's TOR feature should work in combination with other TCP/IP over radio systems, such as JNOS,
Linux, and Flexnet, etc. You don't really need AGWPE on both
ends of a AGWPE TCP/IP system. On this web site, however,
only a pure AGWPE system (both stations using AGWPE) is
discussed. Setting up other TCP/IP systems is beyond the
scope of this site.
|
In addition, SV2DFK (the gateway) has configured
his Windows XP computer using the
Gateway
Configuration instructions below.
Now let us say that SV2BBO (the client) uses his
browser, Internet Explorer 6.0, to request the TAPR web site's
home page at http://www.tapr.org.
Windows automatically forwards this HTTP request to the
SV2AGW TOR adapter on SV2BBO's computer, which encodes
the request in an AX.25 packet which is sent to SV2DFK.
At SV2DFK's station, the packet from SV2BBO
first goes to the SV2AGW TOR adapter, where the
HTTP data request is extracted. The data is then
routed to SV2DFK's dialup adapter which
establishes a connection with SV2DFK's internet
service provider and forwards the HTTP request to
www.tapr.org.
The requested HTTP data from www.tapr.org
is returned first to SV2DFK and then to SV2BBO using the
process in reverse. This same process could also
be used for any other internet TCP/IP service (FTP,
SMTP, POP, etc.).
Note that this process is automatic and requires
no intervention from the gateway, SV2DFK, after he has
setup TOR correctly.
Note 1:
IP address
for each
station in your TOR network. If your network
will be relatively simple and will not tie into
other TCP/IP networks, you can pick your own IP
addresses. Since Amateur Radio has been assigned
the block of IP addresses beginning with "44.",
you should begin your addresses that way
(example: 44.1.1.1 and 44.1.1.2). If
your network may be heard by or tie into other
ham radio TCP/IP networks, you should instead obtain unique
addresses from
AMPRNet.. This will prevent
the routing problems that could develop when two or
more stations use the same IP address.
With TOR installed and configured, the gateway
computer will have two network adapters:
- 1.) the SV2AGW
TOR adapter for the radio network connection
- 2.) a
hardware network interface card (or a software dialup adapter
for modem use) for the
internet connection.
1. Configuring the SV2AGW TOR Adapter
The SV2AGW TOR adapter for a gateway computer should be configured as described in the
TOR driver instructions, except the setting for your
Default
Gateway should be blank (no entry). To check or change it...
In Windows XP: use the
Windows Control
Panel to go to the
Settings: Network Connections
list.
Click on the entry for the AGWPE TOR connection; it may be labeled Local Area Connection or
Local Area
Connection 2 (when you open it you should see "Connect using: SV2AGW TCPIP Over Radio
NDIS Driver"). Click on the the Properties
button and then click on Internet Protocol (TCP/IP).
Remove any IP Address entry next to Default Gateway.
In Windows 98: use the
Windows Control
Panel to go to Network.
On
the Configuration tab's component list,
highlight the TCP/IP-> entry for your
network adapter and press the Properties
button. Open the Gateway tab and
remove any
Installed Gateways.
2. Configuring Your Internet Connection Adapter
Assuming that your connection to your Internet Service Provider (ISP) has
been working OK, don't make any changes in the settings for this
adapter (network card or dialup) other than to enable Internet Connection Sharing (ICS).
In Windows XP: Open the
network connection you use for internet service (either Dialup Connection
or your network card/ Local Area Connection) and then press its
Properties button. Open the
Advanced
tab (at the top) and then check the box for
Internet Connection Sharing.
If it is not there, start the Network Setup Wizard:
click Start, point to Settings, click
Control Panel, and then
double-click Network Setup Wizard.
(Note: If you are not using a hardware or software firewall on your internet
connection, you may also
want to check the Internet Connection Firewall
(ICF). ICF may do some good, but first try TOR without it. If TOR works OK, then
try ICF.)
In Windows 98: Open
Internet Explorer and from the menu select
Tools: Internet Options. At the bottom of
the window, below the LAN Settings button,
press the Sharing button.
If you do not see a
Sharing button, then ICS is not installed.
To install it:
- From the Windows'
Control Panel
open Add/Remove Programs. Select
Windows Settings and then, from
Components List, select Internet Tools. Press the
Details
button and make sure there is a checkmark next to
Internet Connection Sharing. Press the
OK button and then the
Apply button. You will then be prompted to
insert the Windows 98 CD-ROM. After ICS is installed, the ICS Setup Wizard runs
automatically.
- Fill in the choices as follows:
- In the
Internet Connection Sharing window,
select Enable Internet Connection Sharing
and Show Icon (if you want)
- For Connect to the Internet using,
select the network interface card that you
use to connect to your ISP or Dial-Up Adapter
if you connect by telephone.
- For
Connect to my home network using,
select the gateway's SV2AGW TCP/IP adapter.
If you can not get Windows' Internet Connection Sharing feature to work
correctly in Win98/ME, use a proxy server
program on the gateway. The proxy server will handle the data exchange between
the TOR adapter and the dialup/network
adapter. You should be able to find a shareware or freeware proxy server on the internet.
SV2AGW has suggested
HHPROXY, which is freeware.
The proxy server program must be configured and running on the gateway computer when the
client station wants access to the internet from the gateway.
1. Proxy Setup on the Gateway Computer
At the gateway station, the proxy server must be configured with the
gateway's radio network IP address, a "port" to
listen for requests from clients (example: 8080), and information about
the gateway's internet access (dialup info or network card).
As an example, here's the key points in
configuring the HHPROXY program (more info and examples are in the
HHPROXY zip package; do a web search to
find a download site):
1. Set the line Local Name to the radio network IP
address of the station acting as the gateway station.
2. If you are using a dialup connection, use the
examples to help you configure the line below for your setup:
Dial "T-Online" "" ""
0007777777770888888888#0001 ASK "" 180 194.25.2.129 3 30
If you are not using a dialup internet connection, put the
word REM in front of that line.
3. Configure all other protocols as in the sample
configuration file.
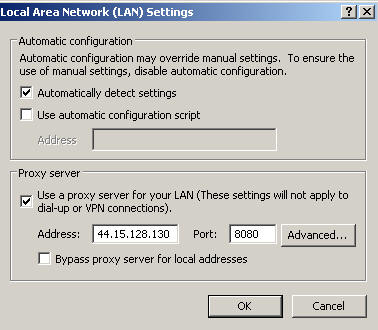
2. Proxy Setup on the Client Computer
The client station must now be configured to use the
gateway station's proxy server. In the client's Internet Explorer 6.0, select
Tools, then Internet Options, then select the
Connections tab.
Then check Use a proxy server for
your LAN and then enter the IP radio network address
for the gateway station and the port number on the gateway station where the
proxy server program can be accessed. (Ask the gateway
ham for these numbers.)
Sample Internet Explorer 6.0 screen shot on the client workstation:
Go To:
TOR: Overview
TOR: Install TOR Virtual
Adapter
TOR: AGWPE Settings
TOR: Windows Settings
TOR: Application Settings |